Cyber Security Interview Questions with Answers (2026)
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity continues to be a vital player. To help you prepare for your upcoming interviews, we've compiled a comprehensive list of common cybersecurity interview questions—ranging from foundational network concepts to advanced cloud security scenarios—complete with insightful answers and strategies.
Understanding the Interview Landscape
With cybersecurity roles becoming increasingly specialized, the interview process has become more rigorous. Companies, especially FAANG and other top-tier cybersecurity firms, are looking for professionals with not just theoretical knowledge but hands-on skills.
This is where platforms like CyberInterviewPrep, with features such as AI-powered mock interviews and secure coding challenges, can be immensely beneficial. But before you jump into the simulator, you need to master the theory.
Here are 20+ top interview questions broken down by category.
Part 1: The Fundamentals (Network & General)
These questions test your understanding of the core building blocks of the internet and security principles.
1. What is the CIA Triad?
Answer: The CIA Triad is the foundational model of information security. It stands for:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring data is accessed only by authorized individuals.
- Integrity: Ensuring data is reliable and hasn't been tampered with.
- Availability: Ensuring data is accessible when needed.

2. What is a DDoS attack, and how can it be prevented?
Answer: A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack involves multiple systems flooding the bandwidth or resources of a targeted system. Mitigation strategies include rate limiting, filtering, using Web Application Firewalls (WAF), and leveraging Anycast networks to disperse traffic.
3. What is the difference between a Vulnerability, a Threat, and a Risk?
Answer:
- Vulnerability: A weakness in the system (e.g., unpatched software).
- Threat: A potential danger that exploits a vulnerability (e.g., a hacker).
- Risk: The potential for loss or damage when a threat exploits a vulnerability.
4. Explain the difference between TCP and UDP.
Answer:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Connection-oriented, reliable, and ensures packets arrive in order (used for HTTP, SSH).
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Connectionless, faster but unreliable, with no guarantee of delivery (used for streaming, VoIP, DNS).
5. What is port scanning?
Answer: Port scanning is a technique used to identify open ports and services available on a network host. It is often used by security administrators to verify network security policies and by attackers to identify potential entry points.
Part 2: Web Application Security
With the rise of SaaS, web app questions are critical for 2026 interviews.
6. What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Answer: XSS occurs when an attacker injects malicious scripts into content that is then viewed by other users. This usually happens when the application does not validate user input properly.
- Remediation: Input validation and output encoding.
7. What is SQL Injection (SQLi)?
Answer: SQLi is a code injection technique where an attacker executes malicious SQL statements that control a web application's database server.
- Remediation: Use prepared statements (parameterized queries) rather than string concatenation.
8. What is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)?
Answer: CSRF forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they are currently authenticated.
- Remediation: Using Anti-CSRF tokens (unique, unpredictable tokens generated by the server).
9. What is a WAF and why is it used?
Answer: A Web Application Firewall (WAF) helps protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. It protects against attacks like XSS, SQLi, and file inclusion.
10. Explain the difference between Authentication and Authorization.
Answer:
- Authentication (AuthN): Verifying who you are (e.g., logging in with a password).
- Authorization (AuthZ): Verifying what you can do (e.g., an admin has permission to delete users, a guest does not).
Part 3: Cryptography & Data Protection
11. How does SSL/TLS work?
Answer: SSL/TLS provides a secure channel between two machines. It uses a "handshake" process where the server presents a certificate to prove its identity (Asymmetric Encryption). Once the identity is verified, a session key is generated to encrypt the actual data transfer (Symmetric Encryption).
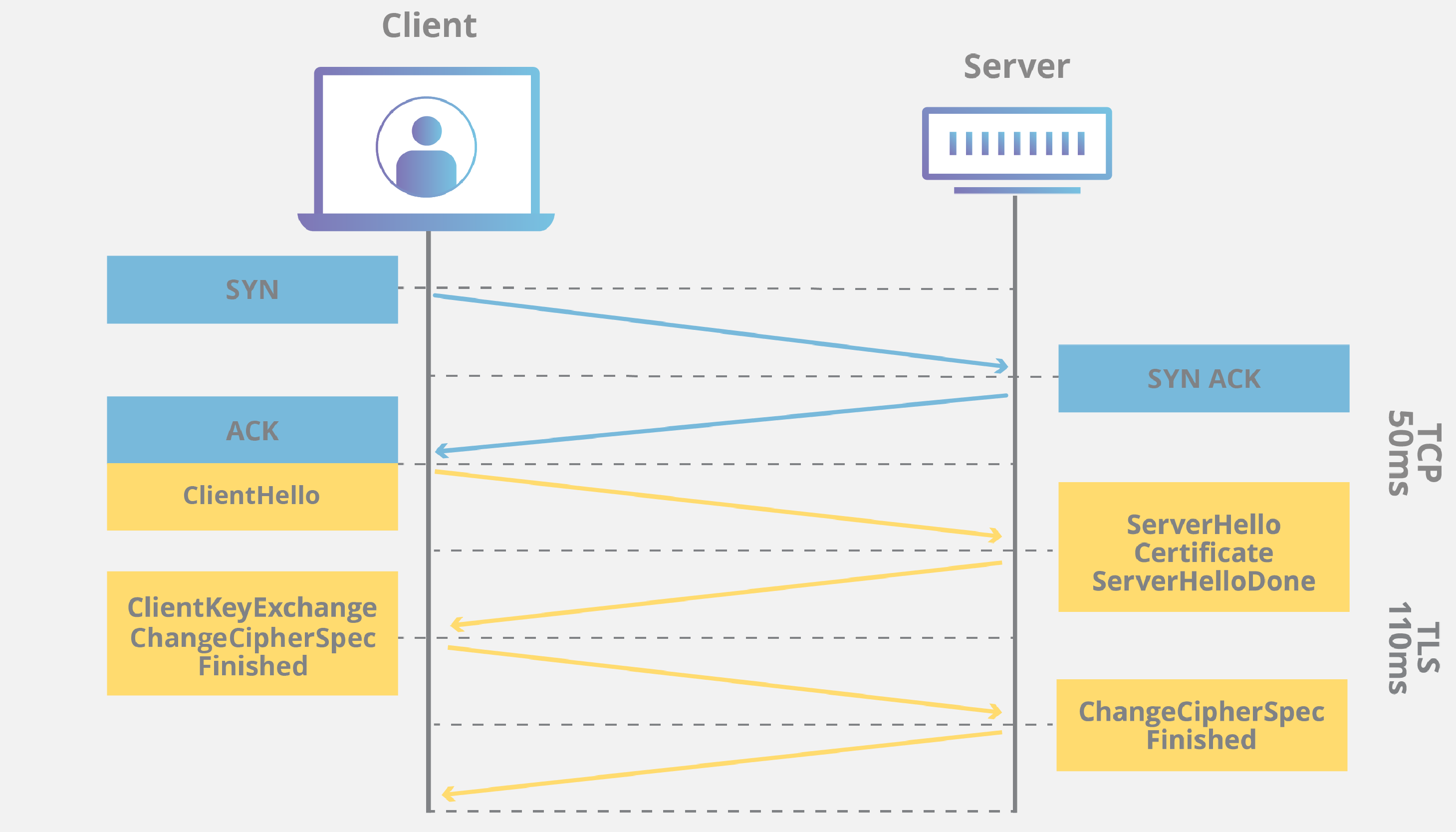
12. What is the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption?
Answer:
- Symmetric: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption (Faster, but key exchange is risky).
- Asymmetric: Uses a pair of keys (Public and Private). One encrypts, the other decrypts (More secure for key exchange, but slower).

13. What is Salting and why is it important in password storage?
Answer: Salting adds a unique, random string of characters to a password before it is hashed. This defends against "Rainbow Table" attacks, where attackers use pre-computed tables of hashes to crack passwords.
14. What is a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack?
Answer: An attack where the perpetrator secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other.
15. What is the difference between Encoding, Encryption, and Hashing?
Answer:
- Encoding: Transforming data to be usable by a different system (Reversible, no key).
- Encryption: Transforming data to keep it secret (Reversible only with a key).
- Hashing: Transforming data into a fixed-length string (One-way, not reversible).
Part 4: Cloud & Advanced Concepts (2026 Trends)
16. What is "Zero Trust" security?
Answer: A security model that assumes no user or device—inside or outside the network—can be trusted by default. Every request must be authenticated, authorized, and encrypted. "Never trust, always verify."
17. What is DevSecOps?
Answer: DevSecOps is the philosophy of integrating security practices within the DevOps process. It involves shifting security "left," meaning addressing security issues early in the development lifecycle rather than at the end.
18. What is a Honeypot?
Answer: A decoy system or server deployed alongside production systems to attract and trap potential attackers. It allows security teams to study the attacker's behavior without risking actual assets.
19. How do you handle a Phishing incident?
Answer: A standard response includes:
- Isolating the infected machine.
- Analyzing the email headers and payload.
- Changing compromised credentials.
- Checking logs to see if data was exfiltrated.
- Notifying the organization and training the user.
20. What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Answer: CSPM tools automate the identification and remediation of risks across cloud infrastructures, such as misconfigured S3 buckets or improper IAM roles.
Part 5: Behavioral & Scenario Questions
21. How do you keep yourself updated with the latest security news?
Answer: Personalize this: Mention reading sources like The Hacker News, following CVE databases, participating in CTFs (Capture The Flags), or using platforms like CyberInterviewPrep for community challenges.
22. You discover a critical vulnerability in a production system on a Friday afternoon. What do you do?
Answer: This tests your judgment.
- Verify: Confirm it is a true positive.
- Assess: Determine the severity and impact.
- Communicate: Inform stakeholders immediately.
- Mitigate: Apply a temporary patch or mitigation if a full fix is too risky to deploy during high traffic.
- Document: Record the incident for future review.
CyberInterviewPrep's Role in Your Success
Preparing for cybersecurity interviews requires a thorough understanding of the industry's current trends and potential scenarios. Reading these questions is a great start, but practice is where you solidify the knowledge.
CyberInterviewPrep offers advanced interview simulations that provide realistic scenarios, allowing you to practice and get feedback. Whether you need mentorship, CV analysis, or flashcards to memorize the ports and protocols mentioned above, we have the tools to build your confidence.




